The world economy is undergoing a seismic shift as digital cryptocurrencies overcome the limits and inefficiencies of government-issued fiat currencies. The new cryptocurrency revolution is poised to bring full economic equity to everyone, with complete access to financial tools that are currently reserved for investment bankers and their wealthy customers.
The new cryptocurrency world was born in the world of computer science, with algorithms and data structures complicated enough to bewilder all but the most advanced software engineers. But today, crypto is available to everyone.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
What is crypto? It depends who you ask. Ask a software engineer to define cryptocurrency and you’ll hear about algorithms and data structures. Pose the same question – “what are cryptocurrencies?” – to bankers and government regulators, and they’ll describe a populist movement that requires a careful response. And to millions of investors, crypto is an opportunity to provide for their futures and their families.
What’s cryptocurrency? It’s a technology, an investment opportunity, and an entirely new way of looking at money. When people say “crypto,” the meaning depends on who they are and how they look at it.
Any cryptocurrency definition must include a bit of history, an overview of the technology, and a survey of the market opportunities. That’s what we provide here: cryptocurrency for beginners, an overview of today’s crypto world and the future it promises.
What does crypto mean? Let’s dive in and find out.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
The “crypto” part of the word “cryptocurrency” refers to the encryption that is provided on all modern digital currencies. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Dogecoin have value because people pay to buy them. Crypto can then be traded for goods, services, or government-issued currencies like euros.
Most people acquire cryptocurrency by purchasing coins and tokens online from exchanges or by selling something and accepting cryptocurrency as payment. Some earn coins by using their computers to validate transactions on the blockchain. The performance of these calculations is rewarded with newly minted coins in a process called mining.
When Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin, the source code specified an arbitrary limit on the total number of Bitcoins that could be minted – about 21 million. At the beginning of 2021, there were only about 2.4 million Bitcoins yet to be created and put into circulation.
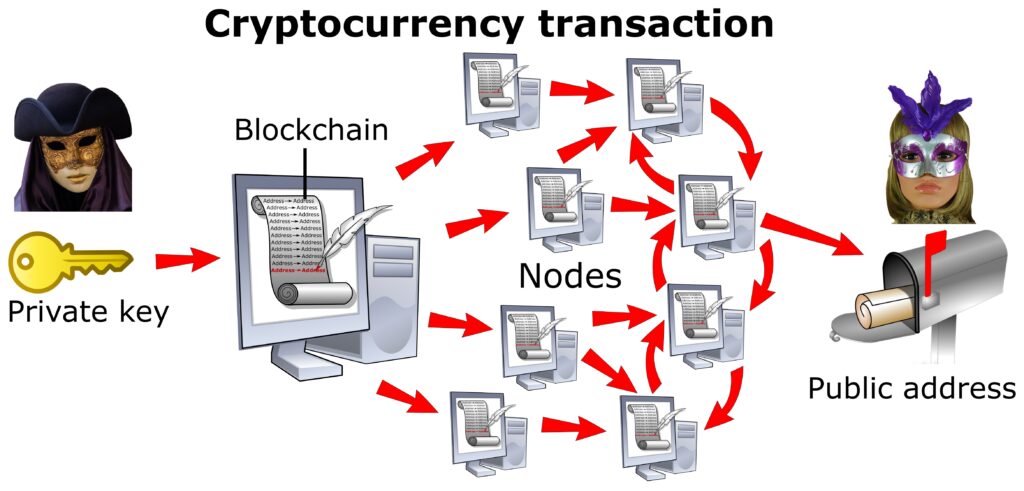
Introductions to cryptocurrency always include the word “blockchain.” A blockchain is a distributed database that tracks cryptocurrency transactions. Although blockchains and cryptocurrency have been entangled since the very beginning, they are different. The blockchain architecture can be used for many purposes besides virtual currency, and digital currencies don’t need to be implemented on blockchains. However, the world’s current cryptocurrencies are based on blockchains because the blockchain architecture offers unique technical benefits. Every digital currency currently trading is a blockchain cryptocurrency.
Coins and Tokens
We tend to use the terms “coin” and “token” interchangeably when referring to units of cryptocurrency, but they are different.
A coin is the native currency of a blockchain. For example, Ether is the coin of the Ethereum blockchain. Crypto coins include Bitcoin, Ripple, Ethereum, Dogecoin, NEO, and Litecoin.
Tokens are coins that are built on another blockchain. Dozens of tokens have been built on the Ethereum blockchain, for instance, including Enjin Coin, SAND, Radix, and Lotto.
One important difference between coins and tokens is that gas – essentially the “tax” on crypto transactions – must generally be paid using the blockchain’s native currency. So if you use SAND or Radix or Lotto, your blockchain transaction charges will be paid in Ether. Conversion and payment may happen automatically in the background or you may need to keep some Ether in your wallet, depending on the token you are working with and the application you are using.
Is Crypto Safe?
News reports make it seem that crypto investors are subject to scams and hack attacks on a regular basis.
Some of these losses occurred years ago at crypto exchanges that did not apply modern security measures to the money they held for customers.
Others are due to software bugs in particular applications, especially DeFi apps.
Despite these attention-getting losses, crypto technology is actually quite secure. Blockchains provide immutable records of transactions, and as long as no one gains access to your account, your crypto funds should be safe.

The Future of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency has the potential to be a populist alternative to the banking system’s monopoly on financial markets and investing. It could bring more than a million unbanked people into the worldwide economy, enabling everyone to benefit from their contributions.
Governments, banks, and investment houses are now experimenting with responses to the growth of cryptocurrency. Some see crypto as a threat, while others see it as a technology that can
coexist alongside conventional financial tools. Some countries encourage crypto use, while others discourage it. Regulations change frequently – as an investor, you should factor such changes into your calculations. Keep up with cryptocurrency news at Kriptomat, your online source of relevant information on the latest events in crypto news.
NOTE
This text is informative in nature and should not be considered an investment recommendation. It does not express the personal opinion of the author or service. Any investment or trading is risky, and past returns are not a guarantee of future returns. Risk only assets that you are willing to lose.




 IOS
IOS Android
Android